Random volume force along the line. More...
 Collaboration diagram for Line tripping module:
Collaboration diagram for Line tripping module:Files | |
| file | tripl.f |
| Tripping function supporting conformal and AMR version of nek5000. | |
Functions | |
| subroutine | tripl_register () |
| Register tripping module. More... | |
| subroutine | tripl_init () |
| Initilise tripping module. More... | |
| logical function | tripl_is_initialised () |
| Check if module was initialised. More... | |
| subroutine | tripl_update () |
| Update tripping. More... | |
| subroutine | tripl_forcing (ffx, ffy, ffz, ix, iy, iz, ieg) |
| Compute tripping forcing. More... | |
| subroutine | tripl_reset () |
| Reset tripping. More... | |
| subroutine | tripl_1dprj () |
| Get 1D projection, array mapping and forcing smoothing. More... | |
| subroutine | tripl_rphs_get |
| Generate set of random phases. More... | |
| real function | tripl_ran2 (il) |
| A simple portable random number generator. More... | |
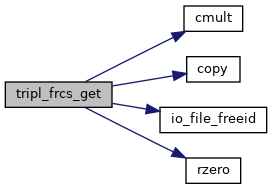
| subroutine | tripl_frcs_get (ifreset) |
| Generate forcing along 1D line. More... | |
Detailed Description
Random volume force along the line.
Set of routines to generate random volume force along the line defined by its starting and ending points. This tool can be used e.g. to mimic sand paper effect by setting a line running in a spanwise direction of the domain. Its aim is to introduce to the flow low amplitude random noise, that can be used to study e.g. a stability of a boundary layer.
Each line can be declared as finate in size (streatching from the starting point to the ending on) or the infinite one. The focing is applied only in the eliptical region along the line defined by the smoothing lengths SMTHX and SMTHY and rotated counterclockwise by ROTA angle. This angel is used as well to rotate the force, so it can be e.g. normal to the wall. In case of a finite length line the smoothing in the third direction SMTHZ is taken into account at the line ending points as well. The forcing is always normal to the line and its direction is not changin along the line. It is just forcing magnitude that fluctuates. As a line direction is specified by its starting and ending points, to determine the forcing direction we define line's local coordinate system build of three versors VX, VY and VZ, where VZ is by definition parallel to the line. To determine versors normal to the line we use vector cross product:
![]()
where VL is a vrsor parallel to the physical y axis for VZ parallel to the physical x axis, and it is parallel to the physical x axis otherwise. Finally
![]()
The last operation is a rotation of the local vresors VX and VY by ROTA angle along VZ versor. The forcing is always directed along VY versor.
The smoothing function is defined in the following way:
![]()
where
![]()
for an infinite line and the interior of the finite line, and
![]()
for the finite line endings. ![]() and
and ![]() are the point coordinates in the line's locall coordinate system, and
are the point coordinates in the line's locall coordinate system, and ![]() is a third local coordinate relative to the corresponding line ending.
is a third local coordinate relative to the corresponding line ending.
However, the function with limitted support can be easily replaced with simple Gauss profile (see commented lines in tripl_1dprj and notice factor 4.0 in the Gauss function necessary to make smoothing lenghts consistent with the original function). The tripping has both steady and unsteeady parts with amplitudes TIAMP and TDAMP respectively, and the forcing is given by:
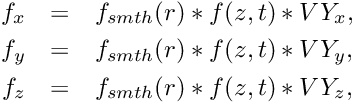
where
![]()
and
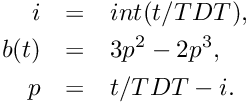
Here ![]() and
and ![]() are Fourier series of unit amplitude with NMODE random coefficients. The trip forcing generates noise with a uniform distribution over all frequencies lower than the cutoff frequency corresponding to
are Fourier series of unit amplitude with NMODE random coefficients. The trip forcing generates noise with a uniform distribution over all frequencies lower than the cutoff frequency corresponding to ![]() , where TDT is a time interval between change of the time dependent part of the trip.
, where TDT is a time interval between change of the time dependent part of the trip.
This forcing has one continuous time derivative and is independent of the time discretisation. It should be independent as well on the simulation details (e.g. number of mpi ranks or restart flag). It is based on a similar implementation in the SIMSON code [2], and is described in detail in [7].
This tool can simulate number of lines with different set of parameters for each line. The maximal number of lines is given by tripl_nline_max in TRIPLD include file. In the same way maximal number of Fouries modes per line is given by tripl_nmode_max parameter. User has to adjust values of these variables before compilation of the code.
- Module interface:
- Global interface list:
- Interface provided:
- Global interface dependency:
- Interface required:
- multiple interfaces from Runtime parameters and Monitoring module modules
- io_file_freeid from Input/output module module (debugging only)
- math_rot3da from Math module
- Module interface usage:
- !======================================================================subroutine userf (ix,iy,iz,ieg)include 'SIZE'include 'NEKUSE' ! FF[XYZ]include 'PARALLEL' ! GLLELinclude 'SOLN' ! V[XYZ]integer ix,iy,iz,iegffx = 0.0ffy = 0.0ffz = 0.0! add trippingcall tripl_forcing(ffx,ffy,ffz,ix,iy,iz,ieg)returnend!======================================================================subroutine userchkimplicit noneinclude 'SIZE' !include 'TSTEP' ! ISTEP, lastep, timeinclude 'INPUT' ! IF3D, PARAM! start framework! monitor simulationcall frame_monitor! for trippingcall tripl_update! finalise frameworkif (istep.eq.nsteps.or.lastep.eq.1) thencall frame_endendifreturnend!======================================================================subroutine frame_usr_registerimplicit noneinclude 'SIZE'include 'FRAMELP'!-----------------------------------------------------------------------! register modulescall tripl_registerreturnend subroutine!======================================================================subroutine frame_usr_initimplicit noneinclude 'SIZE'include 'FRAMELP'include 'SOLN'!-----------------------------------------------------------------------! initialise modulescall tripl_initreturnend subroutine!======================================================================subroutine frame_usr_endimplicit noneinclude 'SIZE'include 'FRAMELP'!-----------------------------------------------------------------------! finalise modulesreturnend subroutine!======================================================================subroutine tripl_forcing(ffx, ffy, ffz, ix, iy, iz, ieg)Compute tripping forcing.Definition: tripl.f:376
- Module parameters:
- Global parameter list:
- Parameters provided by tripl module (include file - TRIPLD):
| Varaible | Type | Runtime parameter | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tripl_nline | integer | _tripl:nline | 0 | Number of tripping lines |
| tripl_tiamp(il) | real | _tripl:tiamp'il' | 0.0 | Time independent amplitude |
| tripl_tdamp(il) | real | _tripl:tdamp'il' | 0.0 | Time dependent amplitude |
| tripl_spos(1,il) | real | _tripl:sposx'il' | 0.0 | Starting point X of 'il' line |
| tripl_spos(2,il) | real | _tripl:sposy'il' | 0.0 | Starting point Y of 'il' line |
| tripl_spos(3,il) | real | _tripl:sposz'il' | 0.0 | Starting point Z of 'il' line |
| tripl_epos(1,il) | real | _tripl:eposx'il' | 0.0 | Ending point X of 'il' line |
| tripl_epos(2,il) | real | _tripl:eposy'il' | 0.0 | Ending point Y of 'il' line |
| tripl_epos(3,il) | real | _tripl:eposz'il' | 0.0 | Ending point Z of 'il' line |
| tripl_smth(1,il) | real | _tripl:smthx'il' | 0.0 | Smoothing length X of 'il' line |
| tripl_smth(2,il) | real | _tripl:smthy'il' | 0.0 | Smoothing length Y of 'il' line |
| tripl_smth(3,il) | real | _tripl:smthz'il' | 0.0 | Smoothing length Z of 'il' line |
| tripl_lext(il) | logical | _tripl:lext'il' | .F. | Line extension |
| tripl_rota(il) | real | _tripl:rota'il' | 0.0 | Rotation angle of 'il' line |
| tripl_nmode(il) | integer | _tripl:nmode'il' | 0 | Number of Fourier modes of 'il' line |
| tripl_tdt(il) | real | _tripl:tdt'il' | 0.0 | Time step for tripping of 'il' line |
- Module parameter usage:
- [_TRIPL] # Runtime paramere section for tripping moduleNLINE = 2 # Number of tripping linesTIAMP01 = 0.00000000E+00 # Time independent amplitudeTDAMP01 = 1.00000000E+01 # Time dependent amplitudeSPOSX01 = 8.30000000E+00 # Starting pont XSPOSY01 = 3.03500000E+00 # Starting pont YSPOSZ01 = 0.00000000E+00 # Starting pont ZEPOSX01 = 8.30000000E+00 # Ending pont XEPOSY01 = 3.03500000E+00 # Ending pont YEPOSZ01 = 4.50000000E+00 # Ending pont ZSMTHX01 = 1.36000000E+00 # Smoothing length XSMTHY01 = 0.34000000E+00 # Smoothing length YSMTHZ01 = 0.00000000E+00 # Smoothing length ZLEXT01 = yes # Line extensionROTA01 = 0.00000000E+00 # Rotation angle in radiansNMODE01 = 16 # Number of Fourier modesTDT01 = 0.14000000E+00 # Time step for trippingTIAMP02 = 0.00000000E+00 # Time independent amplitudeTDAMP02 = 1.00000000E+01 # Time dependent amplitudeSPOSX02 = 8.80000000E+00 # Starting pont XSPOSY02 = 0.99430000E+00 # Starting pont YSPOSZ02 = 0.00000000E+00 # Starting pont ZEPOSX02 = 8.80000000E+00 # Ending pont XEPOSY02 = 0.99430000E+00 # Ending pont YEPOSZ02 = 4.50000000E+00 # Ending pont ZSMTHX02 = 0.28000000E+00 # Smoothing length XSMTHY02 = 0.07000000E+00 # Smoothing length YSMTHZ02 = 0.20000000E+00 # Smoothing length ZLEXT02 = no # Line extensionROTA02 = 0.12300000E+00 # Rotation angle in radiansNMODE02 = 76 # Number of Fourier modesTDT02 = 0.14000000E+00 # Time step for tripping
Function Documentation
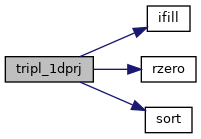
◆ tripl_1dprj()
| subroutine tripl_1dprj |
Get 1D projection, array mapping and forcing smoothing.
This routine supports straight lines given by their starting and ending points. Additional flagg allows to introuduce forcing periodicity or contain it between starting and ending points + smooting lenght in z
- Remarks
- This routine uses global scratch space CTMP0 and CTMP1
Definition at line 445 of file tripl.f.
References ifill(), rzero(), and sort().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ tripl_forcing()
| subroutine tripl_forcing | ( | real | ffx, |
| real | ffy, | ||
| real | ffz, | ||
| integer | ix, | ||
| integer | iy, | ||
| integer | iz, | ||
| integer | ieg | ||
| ) |
◆ tripl_frcs_get()
| subroutine tripl_frcs_get | ( | logical | ifreset | ) |
◆ tripl_init()
| subroutine tripl_init |
Initilise tripping module.
- Note
- This routine should be called in frame_usr_init
Definition at line 135 of file tripl.f.
References cross(), math_rot3da(), mntr_abort(), mntr_log(), mntr_logi(), mntr_logr(), mntr_logrv(), mntr_tmr_add(), mntr_warn(), rprm_rp_get(), rzero(), tripl_1dprj(), tripl_frcs_get(), and tripl_rphs_get().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ tripl_is_initialised()
| logical function tripl_is_initialised |
◆ tripl_ran2()
| real function tripl_ran2 | ( | integer | il | ) |
A simple portable random number generator.
Requires 32-bit integer arithmetic. Taken from Numerical Recipes, William Press et al. Gives correlation free random numbers but does not have a very large dynamic range, i.e only generates 714025 different numbers. Set seed negative for initialization
- Parameters
-
[in] il line number
- Returns
- ran
◆ tripl_register()
| subroutine tripl_register |
Register tripping module.
- Note
- This routine should be called in frame_usr_register
Definition at line 13 of file tripl.f.
References mntr_abort(), mntr_mod_is_name_reg(), mntr_mod_reg(), mntr_tmr_add(), mntr_tmr_is_name_reg(), mntr_tmr_reg(), mntr_warn(), rprm_rp_reg(), rprm_sec_reg(), and rprm_sec_set_act().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ tripl_reset()
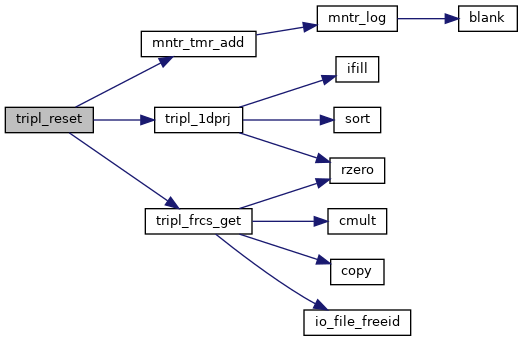
| subroutine tripl_reset |
Reset tripping.
Definition at line 410 of file tripl.f.
References mntr_tmr_add(), tripl_1dprj(), and tripl_frcs_get().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ tripl_rphs_get()
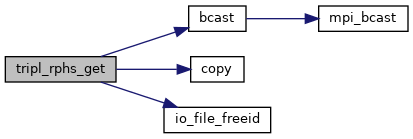
| subroutine tripl_rphs_get |
Generate set of random phases.
Definition at line 568 of file tripl.f.
References bcast(), copy(), and io_file_freeid().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: Here is the caller graph for this function:
Here is the caller graph for this function:◆ tripl_update()
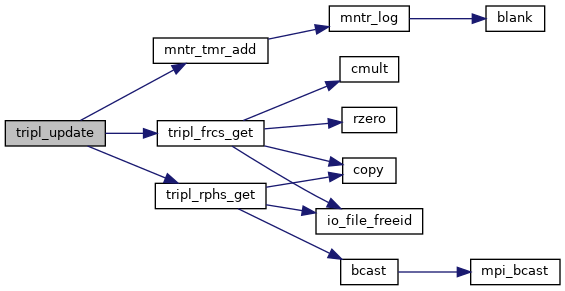
| subroutine tripl_update |
Update tripping.
Definition at line 342 of file tripl.f.
References mntr_tmr_add(), tripl_frcs_get(), and tripl_rphs_get().
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function: